How
1.
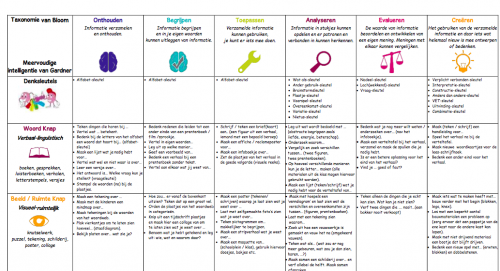
A specific integration matrix from Bloom and Gardner has been developed for pre-school children. This includes questions for various intelligence preferences and different thinking levels, tailored to toddlers.
(de identifying tools van Maruska noemen).
2.
The Australian Tony Ryan invented the concept of Thinker’s Keys in 1990.
They are 20 keys with a question or assignment that encourages children to think creatively, analytically and practically.
Almost all children are familiar with the concept of "key" as a thing you use to open something.
We use the thinking keys to open our minds. This is an easy to explain concept for children.
There is also a video available with explanations.
We present also some projects with topics that are very familiar to young children and that are very useful to differentiate in the questions during the regular lessons.
Thinker's keys makes the lessons and tasks much more interesting and challengin for children with a developmental advantage, and actually for all children!